INTRODUCTION
Solar energy is one of the cleanest and fastest-growing power sources in the world. But many beginners still wonder:
👉 “Solar panel bijli kaise banata hai?”
👉 “Sunlight se electricity kaise generate hoti hai?”
👉 “Solar system mein panels, inverter, battery — sab kya karta hai?”
This simple, beginner-friendly guide explains how solar panels work, step-by-step, with clear examples and easy language.
By the end of this article, you will fully understand how sunlight becomes electricity for your fans, lights, AC, fridge, and home appliances.
1. What Exactly Is a Solar Panel?
A solar panel is a device that converts sunlight into electricity.
It is made of dozens of small units called solar cells.


Each solar cell contains:
- Silicon layers
- Conductive metal contacts
- Anti-reflective coating
Solar cells are arranged in rows to form a complete solar panel.
2. The Science Behind Solar Panels (Very Simple Explanation)
Solar panels use the Photovoltaic Effect (PV effect).
PV Effect Meaning:
When sunlight hits silicon cells → electrons start moving → electricity is produced.
Step-by-step:
- Sunlight = photons
- Solar panel absorbs photons
- Silicon atoms release electrons
- Moving electrons = electricity
- Wires carry electricity to the inverter
That’s it — this is how solar panels generate DC power.
3. What Type of Electricity Do Solar Panels Produce?
Solar panels produce DC (Direct Current) power.
But homes use AC (Alternating Current) power.
So we need an inverter.
4. The Solar Power Flow (Full Journey of Electricity)


Solar Power Journey:
- Sunlight hits panels
- Solar panels generate DC power
- DC goes to inverter
- Inverter converts DC → AC
- AC power runs your home
- Extra power goes to battery or grid (depends on system type)
This is the entire process in simple terms.
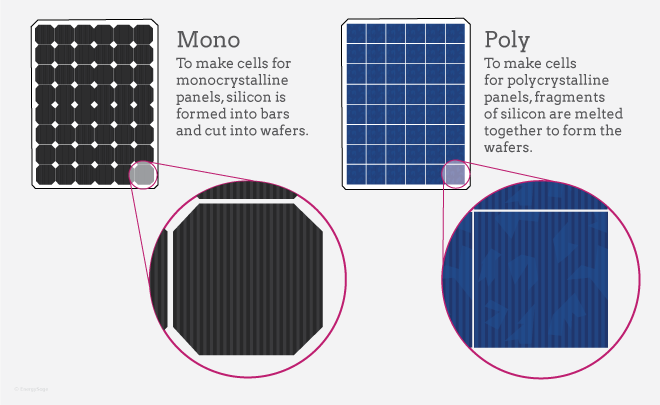
5. Types of Solar Panels (Beginners Must Know)

A) Monocrystalline (Best)
- Highest efficiency
- Best performance in heat
- Long lifespan (25–30 years)
- Black color
Best for: Homes with less roof space.
B) Polycrystalline (Cheaper)
- Lower efficiency
- Blue color
- Good for big rooftops
- Less costly
C) Thin-Film (Rare for homes)
- Flexible
- Lightweight
- Used in portable systems
6. Solar Panel Efficiency Explained (Simple Version)
Efficiency means:
A solar panel converts how much sunlight into electricity?
Example:
A 20% efficiency panel uses 20% of sunlight to produce electricity.
2025 modern panels:
- 21% to 24% efficiency (Monocrystalline)
- 17% to 20% efficiency (Polycrystalline)
Higher efficiency = more power.
7. Solar System Components (Easy Breakdown)

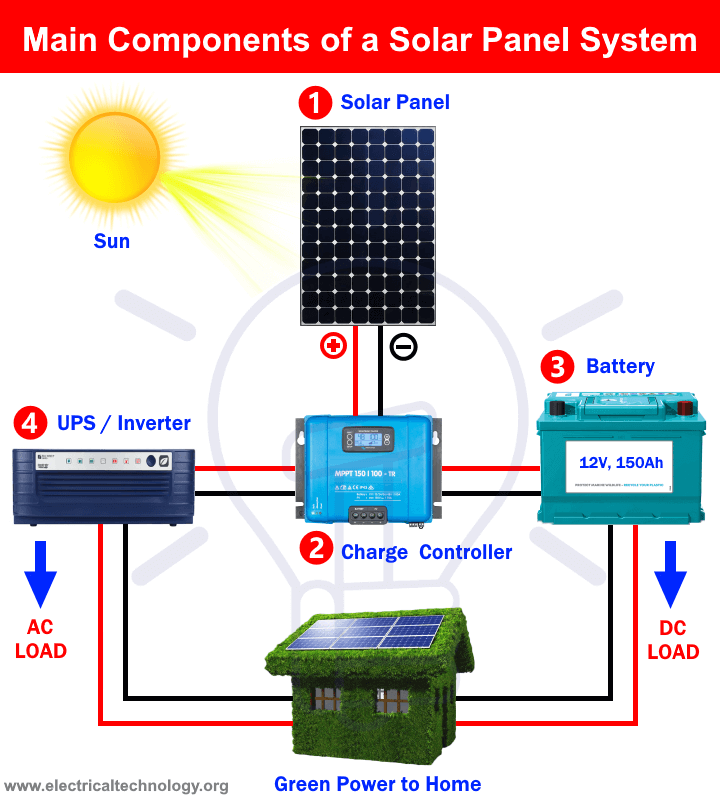
1. Solar Panels
Produce DC electricity.
2. Solar Inverter
Converts DC → AC.
Most important component after panels.
Types:
- On-grid inverter
- Off-grid inverter
- Hybrid inverter
3. Solar Batteries
Store electricity for night or load-shedding.
Types:
- Lithium (best)
- Lead-acid
4. Charge Controller (Off-grid)
Protects battery from overcharging.
5. Mounting Structure
Holds panels at the correct angle.
6. Wiring & Protection Devices
MC4 connectors, breakers, fuses, surge protection.
8. How Does a Solar System Work? (By System Type)
A) On-Grid System (No batteries)
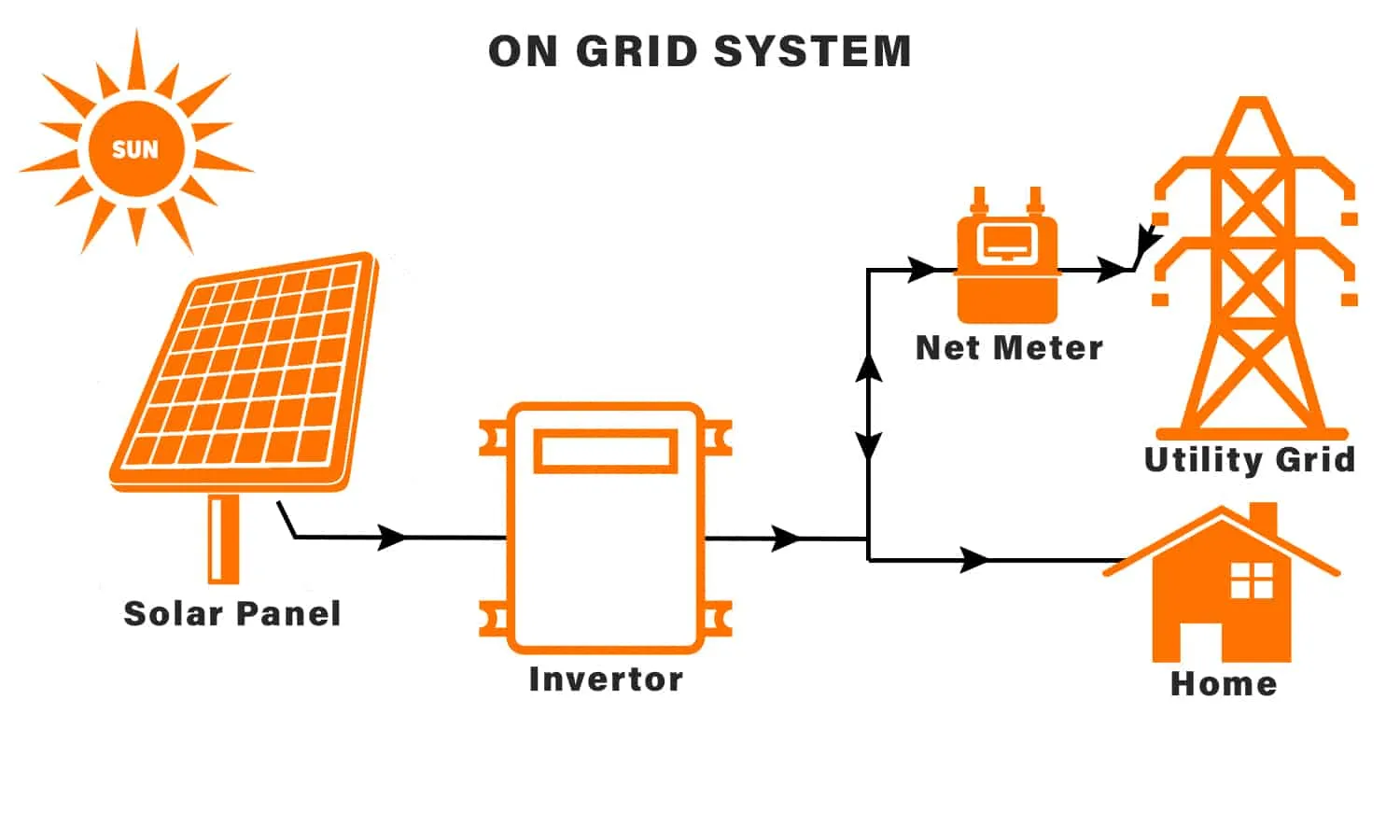

How it works:
- Solar panels produce AC power through inverter
- Home uses solar electricity
- Extra electricity goes to the grid
- Electricity bill reduces via net metering
Best For:
- Cities with stable electricity
- Maximum bill saving
B) Off-Grid System (Only batteries)
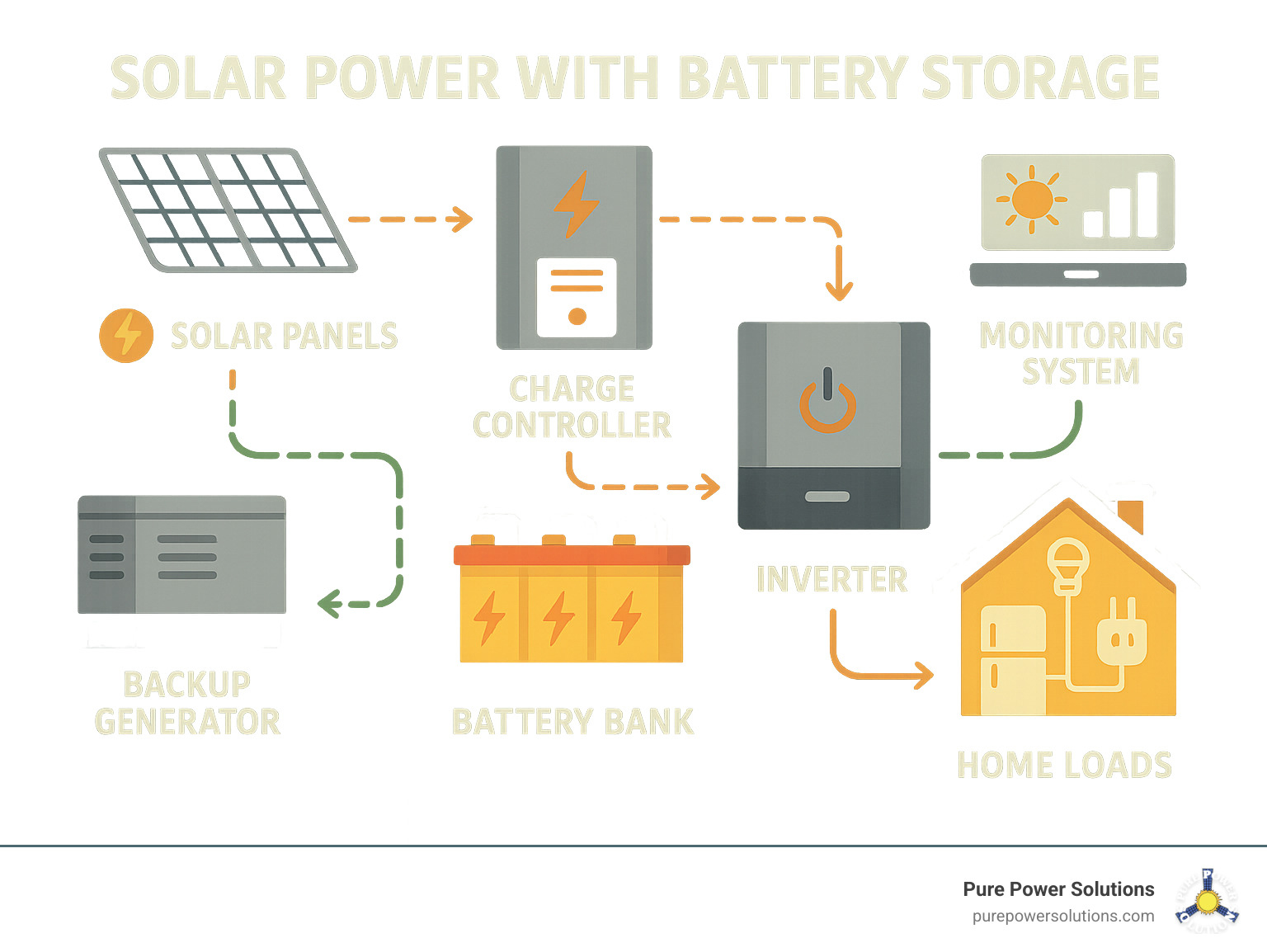

How it works:
- Panels charge the battery
- Battery powers the home
- No grid connection
Best For:
- Villages
- Remote areas
- Homes with heavy load-shedding
C) Hybrid System (Best of both)


How it works:
- Solar runs your home
- Extra charges battery
- More extra goes to the grid
- During outages → battery powers home
Best For:
- Backup + Bill saving together
- Modern homes
9. How Much Energy Does a Solar Panel Produce?
It depends on:
✔ Sunlight hours
✔ Panel wattage
✔ Temperature
✔ Efficiency
✔ Shading
Example:
A 450W solar panel produces:
- 450W × 5 hours sunlight
= 2250 Wh = 2.2 units per day
So 10 panels = 22 units/day.
10. Factors That Affect Solar Panel Performance
- Dust
- Shade
- Heat
- Poor wiring
- Wrong angle
- Cloudy weather
Keeping panels clean increases production by 10–20%.
11. Do Solar Panels Work in Clouds or Rain?
YES.
But production reduces by 40–60%.
Solar panels still generate electricity as long as there is daylight.
12. Benefits of Using Solar Panels

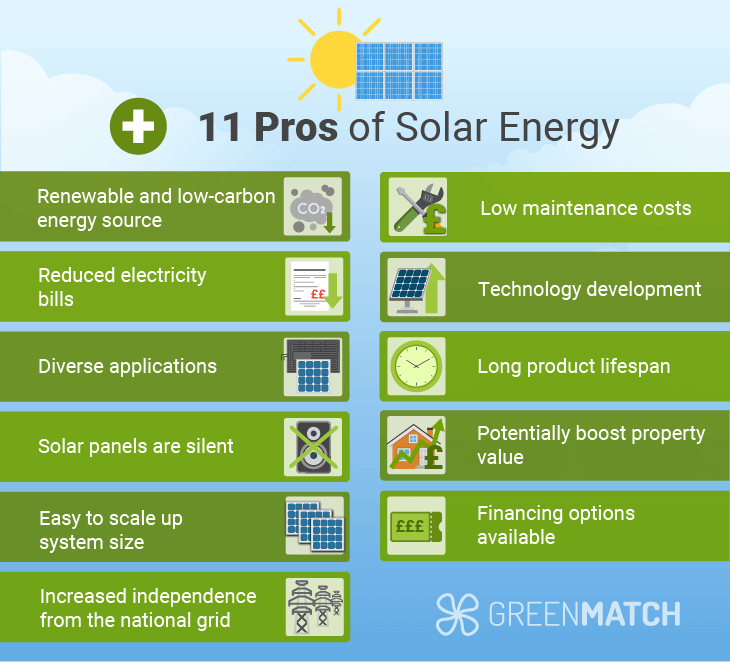
✔ Save 50–100% on bills
✔ 25+ years lifespan
✔ Clean & renewable
✔ Low maintenance
✔ Home value increases
✔ Protection from rising electricity prices
13. Common Myths About Solar Panels (Explained Simply)
❌ Myth 1: Solar doesn’t work in winter
✔ Works — only production decreases slightly.
❌ Myth 2: Solar requires daily maintenance
✔ Only cleaning once a month is enough.
❌ Myth 3: Solar stops working when it is cloudy
✔ Works — just lower output.
❌ Myth 4: Solar systems are too expensive
✔ Prices dropped 70% in last 10 years.
14. Best Solar Panels for Beginners (2025)
✔ LONGi
✔ Jinko
✔ Trina
✔ Canadian Solar
✔ SunPower (premium)
15. Simple Summary for Beginners
Solar panels work by:
- Capturing sunlight
- Generating DC power
- Inverter converts to AC
- AC powers your house
- Extra goes to battery or grid
This is the entire working process — simple and clear.
Conclusion
Solar panels are an amazing investment for homes in 2025. Understanding how they work helps you choose the right system, maintain it better, and get maximum savings.
Whether you choose on-grid, off-grid, or hybrid — the core working principle stays the same.
Sunlight → DC Power → Inverter → AC Power → Your Home
Solar energy is the future — clean, powerful, and economical.









